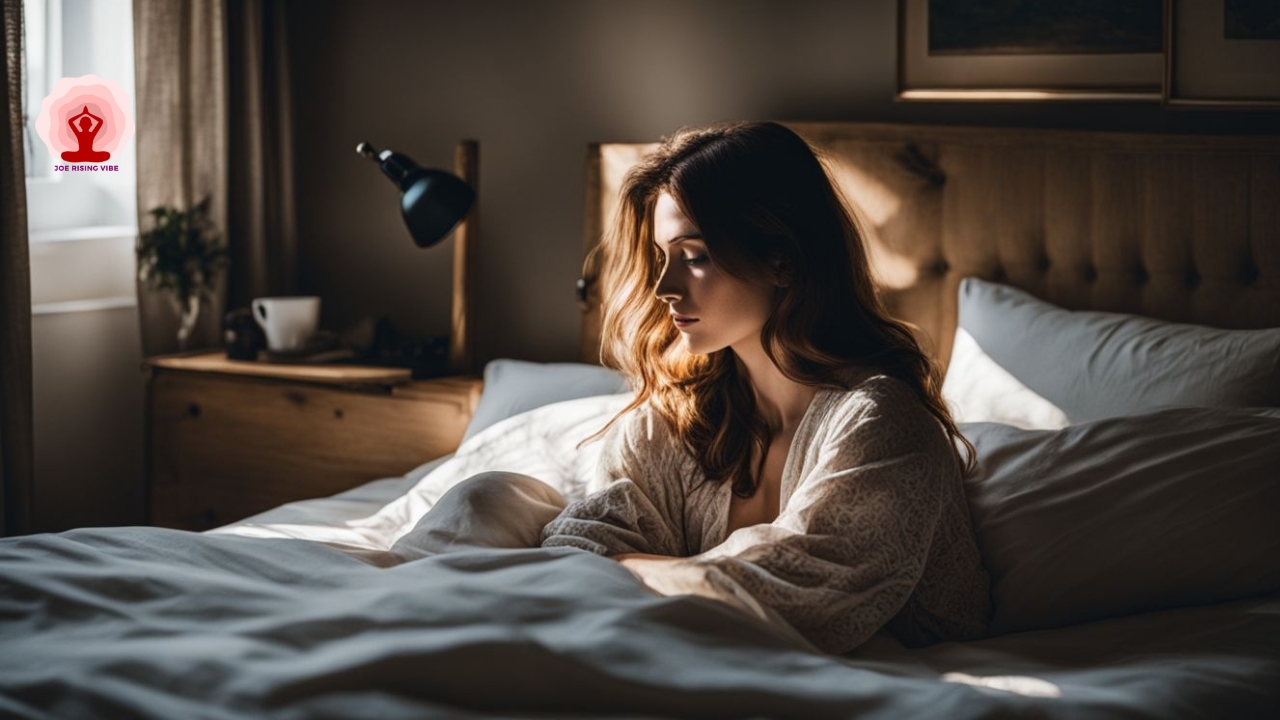
Has the chilling grip of sleep paralysis ever held you captive in the twilight between wakefulness and dreams?
Surprisingly, this state can be the perfect starting point for a journey into conscious dreaming.
This blog offers guidance on harnessing sleep paralysis to enter lucid dreams, giving you control over your dreamscapes.
Understanding Sleep Paralysis
Sleep paralysis is a temporary inability to move or speak that occurs when waking up or falling asleep. Symptoms may include a feeling of pressure on the chest, hallucinations, and intense fear.
While anyone can experience sleep paralysis, it is more common in people with mental health conditions and those who have disrupted sleep patterns.
Definition and explanation
Sleep paralysis happens when you can’t move or speak as you’re waking up or falling asleep. It’s not harmful and usually passes in a few seconds or minutes, but it can be scary. Imagine your mind is wide awake, but your body won’t budge — that’s what sleep paralysis feels like.
During this time, some people see things that aren’t there, like the old hag from myths. Others feel a weight on their chest or think something is holding them down.
This condition ties to REM sleep, the dream stage of our sleep cycle. Our muscles relax during REM sleep so we don’t act out dreams. Sleep paralysis occurs if this muscle relaxation lingers as you start to wake up or drift off to doze.
You become stuck between dreaming and being awake – alert in mind but paralyzed in body. People with narcolepsy or disrupted sleeping patterns are more likely to experience it than others.
Symptoms and signs
Sleep paralysis can make you feel stuck and scared. It happens after falling asleep or when waking up. Here are some common symptoms and signs:
- Being unable to move or speak: You’re awake but can’t move a muscle.
- Pressure on your chest: It feels like someone is sitting on you.
- Hallucinations: You might see or hear things that aren’t there, like shadows or strange noises.
- Difficulty breathing: You may feel like it’s hard to breathe deeply.
- Fear and panic: Many people feel very scared during an episode.
- Sensing a presence: Some think there’s someone else in the room with them.
- Imagined sounds: Noises such as humming or static might fill your ears.
- Feeling fully aware: Even though you can’t move, you know exactly what’s happening around you.
- Temporary paralysis: The inability to move lasts just a few moments, but it seems longer.
Who gets sleep paralysis?
Sleep paralysis can strike anyone. It’s more common in teens and young adults, though. People with sleep problems like narcolepsy or insomnia may experience it more often. Those facing stress or big life changes might also have episodes of paralysis.
Even if you’re healthy, you could wake up feeling stuck.
Having a sleep disorder such as sleep apnea increases the chances too. Mental conditions like anxiety disorders and PTSD can play a role in who gets it. Lifestyle factors matter; using substances or not getting enough rest may trigger an episode.
Genetics can be involved—if family members have had it, your risk goes up.
The Link between Sleep Paralysis and Lucid Dreaming
During sleep paralysis, the body remains in a state of temporary muscle paralysis while the mind is fully conscious. This transitional state from wakefulness to dreaming can serve as a gateway to lucid dreaming, where individuals have heightened control and awareness within their dreams.
The phenomenon occurs during the rapid eye movement (REM) stage of sleep, when dreams are typically most vivid and immersive.
The transition from paralysis to lucidity
Transitioning from sleep paralysis to lucid dreaming is a process that requires overcoming fear and maintaining calm. Overcoming the initial panic during paralysis allows individuals to shift their focus towards dream visualization, an essential step in entering a lucid dream state.
Studies have shown that successfully turning sleep paralysis into a lucid dream can be facilitated through techniques such as the Sleep Paralysis Induced Lucid Dream (SPILD) method, which empowers individuals to utilize the experience safely and enter the world of lucidity.
It’s important to recognize that fear is often a significant barrier in transitioning from sleep paralysis to lucidity. The Wake-Initiated Lucid Dream (WILD) technique emphasizes the need for relaxation and clear mental imagery while going through this transition.
The role of REM sleep
During REM sleep, our brains experience heightened activity and vivid dreaming. This stage plays a critical role in facilitating the transition from paralysis to lucid dreams. It is marked by rapid eye movements, increased brain waves, and temporary muscle paralysis, creating an ideal environment for lucid dreaming experiences.
The link between sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming is directly connected to the unique characteristics of REM sleep, which include heightened awareness and emotional intensity. Additionally, during this stage, the brain’s ability to process emotions and memories makes it conducive for inducing lucidity during episodes of sleep paralysis.
Techniques for Lucid Dreaming from Sleep Paralysis
Maintaining calm during sleep paralysis and focusing on dream visualization are essential techniques for lucid dreaming from sleep paralysis. By utilizing the temporary state of paralysis as a gateway to lucid dreams, individuals can learn to control their dreams and navigate through different dream scenarios.
Maintaining calm during paralysis
To maintain calm during paralysis, focus your attention inwards and remind yourself that it is a temporary state. Use mindfulness techniques to stay centered and affirm to yourself that you are experiencing sleep paralysis.
Techniques such as relaxation, closing your eyes, and consciously entering a state of calm can help ease any anxiety or fear. Understanding that sleep paralysis is part of the process leading to a lucid dream can provide reassurance and help manage the experience more effectively.
Remembering that staying calm is essential for turning sleep paralysis into a lucid dream will also aid in maintaining composure during this phase. Acknowledge the temporary nature of sleep paralysis and use it as an opportunity to transition into a vivid lucid dreaming experience by practicing these calming techniques.
Focusing on dream visualization
Keep calm during sleep paralysis and shift focus inwards, utilizing intentionality to transform the experience into a lucid dream. Use imagery and mental rehearsal to visualize specific dream scenarios, guiding the transition from paralysis to a vivid dream state.
By maintaining a proactive and positive mindset during sleep paralysis, individuals can harness this altered state of consciousness as an entryway into lucid dreaming, enhancing their control over the dream environment and experiences.
Utilizing sleep paralysis as a gateway to lucid dreams
By overcoming fear during sleep paralysis, individuals can transition into lucid dreams. Positive correlations have been found between sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming, suggesting a complex relationship.
The Sleep Paralysis Induced Lucid Dream (SPILD) technique aims to help individuals take advantage of sleep paralysis to enter a lucid dream, utilizing the dissociated experience related to rapid eye movement (REM) sleep.
Maintaining calm during paralysis is crucial for transitioning into a lucid dream. Studies have shown that there are commonalities and distinctions between sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming, related to REM sleep.
Managing Sleep Paralysis for Lucid Dreaming

Prevention strategies and treatment options can help individuals manage sleep paralysis for lucid dreaming, while cognitive-behavior therapy may provide further support. Learn how to maximize your dream potential through effective management techniques.
Prevention strategies
To prevent sleep paralysis, improving sleep hygiene is crucial. This includes maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, creating a comfortable sleeping environment, and avoiding caffeine and electronic devices before bedtime.
Performing reality checks can also help train the mind to recognize consciousness, potentially lessening the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis. Additionally, managing stress through relaxation techniques like meditation or deep breathing can contribute to better overall sleep quality, reducing the risk of episodes.
Focusing on healthy lifestyle habits such as regular exercise and a balanced diet can positively impact both the frequency and severity of sleep paralysis. Lastly, seeking professional help for any underlying sleep disorders or mental health concerns can provide valuable support in preventing recurrent episodes of sleep paralysis.
Treatment options
- Psychopharmacological treatments utilizing tricyclic antidepressants and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors are effective for managing sleep paralysis and promoting lucid dreaming.
- Cognitive – behavior therapy, alongside these medications, helps in addressing the psychological aspects of sleep paralysis and facilitates the transition to lucid dreaming by reducing anxiety and fear.
- Therapy involving lucid dreaming can aid in treating conditions such as recurring nightmares and post-traumatic stress disorder, offering potential benefits for physical rehabilitation and mental health.
- Prevention strategies
- Focus on maintaining a consistent sleep schedule to reduce the likelihood of sleep paralysis episodes.
- Create a relaxing bedtime routine that promotes deep, uninterrupted sleep.
- Avoiding stimulants like caffeine or alcohol close to bedtime can decrease the risk of experiencing sleep paralysis.
- Managing post – episode anxiety
- Engage in calming activities such as deep breathing or meditation to alleviate anxiety following a sleep paralysis episode.
- Seek professional support from therapists or counselors specializing in sleep disorders to address any lingering emotional distress.
- Educate oneself about the nature of sleep paralysis through reliable sources to foster understanding and reduce fear associated with these experiences.
Cognitive-behavior therapy
Cognitive-behavior therapy (CBT) is a proven method for managing sleep paralysis and the associated anxiety, paving the way for lucid dreaming. Through CBT, individuals can learn to reframe negative thought patterns and develop coping strategies to ease the anxiety linked with sleep paralysis episodes.
This treatment approach targets specific behaviors and beliefs, empowering individuals to confront and overcome their fears related to these experiences.
Additionally, research indicates that cognitive-behavioral therapy has been effective in addressing anxiety disorders often accompanying sleep paralysis. By equipping individuals with practical tools and techniques, CBT not only aids in managing anxiety but also contributes to creating a conducive mental environment for achieving lucid dreams during future episodes of sleep paralysis.
How to Take Care of Yourself after a Sleep Paralysis Episode
After experiencing a sleep paralysis episode, it’s important to manage any post-episode anxiety and prepare for future occurrences. Ensuring a healthy sleep routine can also help minimize the likelihood of future episodes.
Managing post-episode anxiety
Managing post-episode anxiety after experiencing sleep paralysis is crucial for overall well-being. Practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing and mindfulness can help alleviate the distress caused by the episode.
Creating a supportive environment, seeking counseling, and understanding that the experience is not harmful are essential in reducing anxiety levels.
Additionally, engaging in self-care strategies like maintaining a consistent sleep schedule and incorporating stress-reducing activities into daily routines can contribute to managing post-episode anxiety effectively.
Preparing for future episodes
Manage post-episode anxiety by practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing and progressive muscle relaxation. Establish a soothing bedtime routine to promote better sleep quality, including avoiding screen time before bed and maintaining a comfortable sleeping environment.
Ensure a healthy sleep routine with consistent bedtimes and wake-up times, aiming for 7-9 hours of sleep each night. Prevent future episodes by reducing stress through mindfulness exercises like meditation or yoga.
Prepare for potential episodes by learning about the science behind sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming to feel more in control during these experiences. Plan ahead by having a trusted person to talk to about your struggles with sleep paralysis, providing emotional support when needed without judgment.
Ensuring a healthy sleep routine
A healthy sleep routine is crucial in managing sleep paralysis. Consistent bedtime and waking schedules, along with creating a comfortable sleep environment, can help improve sleep quality, reduce the incidence of sleep paralysis episodes, and promote overall well-being.
Additionally, engaging in regular physical activity during the day and avoiding stimulants like caffeine close to bedtime can contribute to better sleep patterns and diminish the likelihood of experiencing disruptive episodes.
By prioritizing a balanced lifestyle that includes sufficient rest, individuals may effectively mitigate the occurrence of unsettling occurrences such as sleep paralysis. Notably, practicing relaxation techniques before bed such as meditation or deep breathing can aid in unwinding both body and mind for a more serene slumber experience.
Conclusion
Embracing calmness during sleep paralysis is crucial for transitioning into a lucid dream. By focusing on visualization and maintaining a positive mindset, you can harness the potential of sleep paralysis for lucidity.
Remember, overcoming fear is key to unlocking the power of lucid dreaming from sleep paralysis. With the right techniques and mindset, turning sleep paralysis into a gateway to lucid dreams is within reach.
FAQs
1. What is sleep paralysis and how does it relate to lucid dreaming?
Sleep paralysis is when you’re awake but can’t move or speak as you’re falling asleep or waking up. It’s related to REM (rapid eye movement) sleep, where dreams happen. Sometimes, people use this time to try and start a lucid dream.
2. Can anyone learn to lucid dream during sleep paralysis?
Yes, with practice, many people can learn to control their dreams during sleep paralysis by recognizing the signs and using techniques that help them become aware they are dreaming.
3. Does lack of sleep increase the chances of experiencing sleep paralysis?
Not getting enough sleep can make it more likely for someone to have an episode of sleep paralysis since it disrupts normal REM cycles.
4. Are there any risks in trying to lucid dream from a state of sleep paralysis?
Lucid dreaming from sleep paralysis is generally safe, but if someone has conditions like narcolepsy or experiences extreme anxiety, they should talk with a doctor first.
5. What steps can I take if I want to have a lucid dream starting from a moment of sleep paralysis?
To turn your experience into one where you’re in charge of your dreams, stay calm during the paralyzed state and focus on imagining vivid scenarios until your mind starts dreaming while still aware you’re asleep.
6. Should I see a doctor if my attempts at turning my night terrors into pleasant lucid dreams fail due to constant disruptions like cataplexy?
If problems like cataplexy disturb your ability to control nightmares through attempting controlled dreams and affect your daily life negatively, then yes, seeing a doctor could uncover underlying health issues needing attention.
7. How can you lucid dream without getting sleep paralysis?
To avoid sleep paralysis while lucid dreaming, focus on reality checks throughout the day, encouraging heightened self-awareness. Incorporate a consistent dream journal to recognize recurring patterns and triggers, enhancing the likelihood of lucid dreams without encountering sleep paralysis.
8. How can you lucid dream from sleep paralysis?
When faced with sleep paralysis, maintain composure and shift focus to imaginative and positive thoughts. Instead of succumbing to fear, gently transition your mental state to construct a dream scene, enabling a seamless entry into a lucid dream from the confines of sleep paralysis.
9. Is it possible to lucid dream after sleep paralysis?
Overcoming sleep paralysis-induced fear is crucial for subsequent lucid dreaming. Cultivate a positive mindset, affirming control over your dreams, and persist in practicing lucid dreaming techniques. With perseverance, it’s entirely possible to turn a challenging sleep paralysis experience into a platform for lucid dreaming.