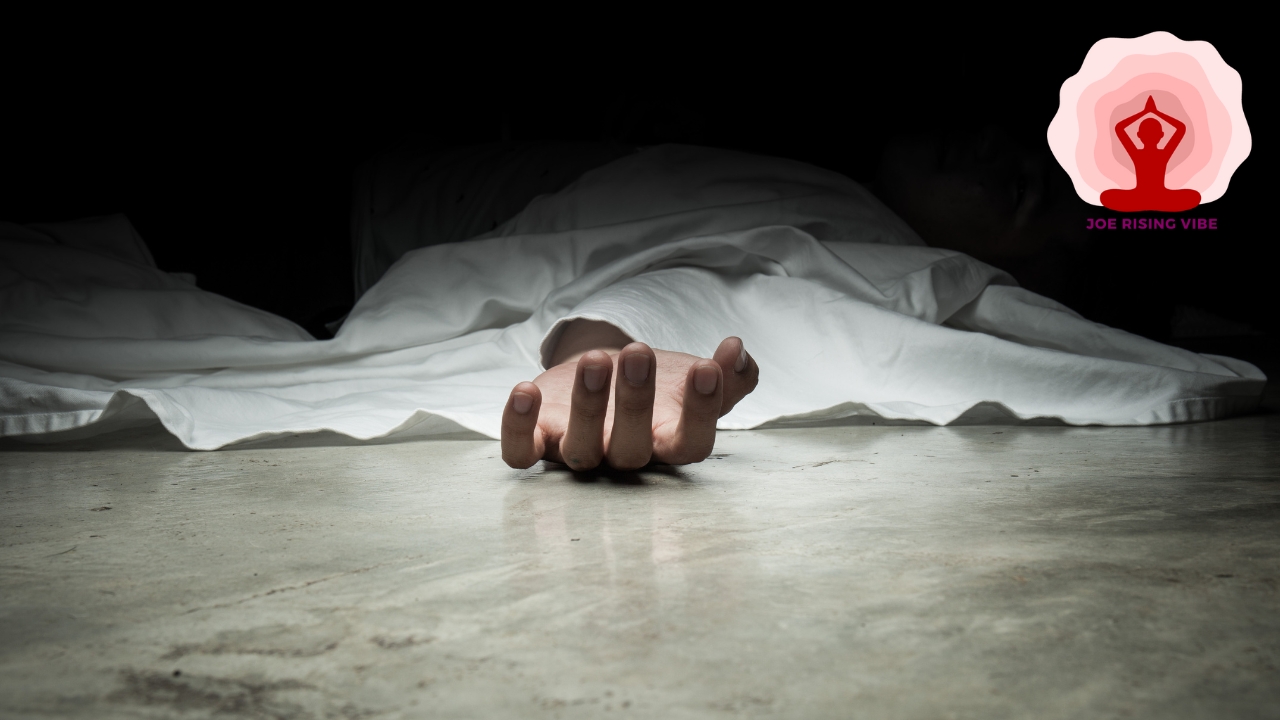
Have you ever wondered what happens when we’re on the brink of death? Near-death experiences (NDEs) are mysterious encounters that some people report after surviving life-threatening situations.
Let’s dive into the fascinating world of NDEs, exploring their common features and the impact they have on those who experience them – a phenomenon that straddles the line between science and the unknown.
Defining Near Death Experience (NDE)
A Near Death Experience (NDE) happens to some people who come close to dying, or during situations where they could have died but did not. People report different feelings and visions in NDEs.
Some see a bright light or feel peacefulness, while others have an out-of-body experience. During these moments, individuals might meet loved ones who have passed away or sense a strong spiritual connection.
Many folks say NDEs change their lives forever. They often lose their fear of death and believe strongly that there’s something more after life ends on Earth. Scientists study these experiences closely, trying to understand the mystery behind them.
Studies involve heart attack survivors and other patients who recall NDEs after being brought back from the brink of death by doctors’ efforts.
Characteristics of Near Death Experiences
Near Death Experiences (NDEs) are marked by common elements and stages, often occurring in clinical circumstances such as cardiac arrest. These experiences can include sensations of peace, out-of-body perceptions, and encounters with light or deceased loved ones.
Common Elements
Many near-death experiences share similar features. People often report feeling pain-free during these events. They describe floating above their bodies, observing what’s happening around them.
This is known as an out-of-body experience. A bright light appears far away to some and they feel drawn towards it. It looks like a tunnel with a shining end.
Others mention deep emotions that fill them with peace or love. Some see visions of deceased relatives or spiritual figures. These moments bring understanding and comfort to many who experience them.
Different beliefs about life after death can shape what people see and feel during these experiences.
Stages
Near death experiences unfold in distinct stages. Each stage brings its own unique elements.
- Initial resistance: At the very start, people often fight the experience. They feel a surge of fear or anxiety as they sense something unusual is happening.
- Surrender: After resisting, individuals may give in to the experience. A sense of calm washes over them, replacing any fear they felt before.
- Out-of-body experience: During this part, many report floating above their bodies. They see everything around them from a new perspective.
- Moving through a tunnel: Experiencers describe traveling through a dark space. They move toward an inviting light at the end.
- Encountering light or beings: Some meet beings made of light or see deceased loved ones. These encounters often bring feelings of love and comfort.
- Life review: In this moment, individuals witness their life’s events flash before them. This can happen rapidly and with great detail.
- Reaching a boundary: Many mention coming to a point they cannot cross unless they fully pass away.
- Coming back: The final stage is returning to their body. People often wake up recalling what they went through as if it was real.
Clinical Circumstances
During cardiac arrest, near-death experiences can occur when the person is unconscious or clinically dead. Life-threatening events like blunt trauma or heart attacks may trigger near-death experiences.
Near-death experiences are also known to be triggered by shocks from blood loss and other life-threatening situations.
A person experiencing a near-death experience may be comatose or clinically dead but can still undergo profound and vivid perceptual experiences. These experiences can include encountering a tunnel of light, out-of-body sensations, and a sense of timelessness.
Near Death Studies
Clinical research in cardiac arrest patients has provided valuable insights into the phenomenon of near-death experiences, shedding light on the cognitive and neurological aspects of these remarkable events.
To delve deeper into the fascinating world of NDEs, continue reading to uncover the latest findings and perspectives on this intriguing topic.
Clinical Research in Cardiac Arrest Patients
Clinical research in cardiac arrest patients has revealed that some individuals report clear and lucid experiences despite being seemingly unconscious during the event. Studies have shown that near-death experiences often accompany cardiac arrest, with patients reporting seeing deceased family members and feeling aware of CPR procedures.
Research on survivors of cardiac arrest has identified different types of near-death experiences, shedding light on the level of awareness during these events.
During Dutch prospective studies on near-death experiences in survivors of cardiac arrest, 18% of patients reported such an experience. Additionally, brain activity during life-saving CPR in some cardiac arrest patients may indicate a near-death experience.
Parnia’s Study in 2001
In 2001, Dr. Parnia conducted a comprehensive study exploring near-death experiences (NDEs). The qualitative and quantitative study aimed to elucidate individuals’ NDEs and identify common themes associated with the phenomenon.
This landmark study concluded that the themes related to the experience of death are more expansive than previously understood, acknowledging the diverse cultural and religious backgrounds of NDE survivors.
It emphasizes the imperative need for standardized guidelines when studying death and recalling such near-death experiences.
Van Lommel’s Study
Van Lommel\’s study, focusing on cardiac arrest survivors, grouped them based on near-death experiences (NDEs). Results were categorized into emotional, cognitive, religious, spiritual aspects of NDEs.
The review supports cardiologist Pim van Lommel\’s claim for human existence continuity presented in ‘Consciousness..’ and offers insights into the details of near-death experiences.
The study delves into situations like cardiac arrest in MI and blood loss shocks. It also explores the continuity of consciousness. A new study recorded brain waves during resuscitation to investigate brain activity related to near-death experiences.
Awareness during Resuscitation (AWARE) Study
The AWARE Study explores consciousness and awareness during cardiac arrest and resuscitation, shedding light on what people experience near death. It has identified four types of experiences during resuscitation, including CPR-induced consciousness (CPRIC) and post-resuscitation encounters.
Furthermore, AWARE-II involved 567 men and women who survived cardiac arrest in hospitals, revealing that some patients recalled death experiences after the event. This research provides valuable insights into cognitive thought processes at the end of life.
Examining hundreds of survivors’ experiences during cardiac arrest, the AWARE study dives deep into understanding mental aspects at the brink of death. By closely investigating these phenomena, it sparks further exploration into cognition during resuscitation and generates a better comprehension of near-death occurrences.
AWARE II
The AWARE II study brought forth specific hypotheses regarding near-death experiences, particularly focusing on consciousness and awareness. This comprehensive investigation yielded four distinct categories of experiences that came to light, encompassing emergence from coma during CPR and post-cardiac arrest occurrences.
Furthermore, the multi-center study centered on consciousness and awareness in CPR patients provided new evidence concerning near-death experiences, adding substantive findings to the expanding body of research in this realm.
This meticulous exploration in the AWARE II study unraveled essential insights into near-death experiences by delving into consciousness and awareness within the context of CPR patients.
Meditation-induced NDEs
Meditation-induced near-death experiences (MI-NDEs) are attracting empirical research attention. Advanced Buddhist meditators suggest that meditation-induced NDEs alter time-space perception.
The University of Derby’s study demonstrated the induction of NDEs through meditation, with wider impact implications. A group can apparently induce NDEs at will via mindfulness meditation, noted in a Mindfulness journal publication.
Currently uninvestigated by any study, MI-NDEs have roots in ancient Buddhist texts.
Explanatory Models for Near Death Experiences
Various explanatory models have been proposed to understand the phenomenon of near-death experiences, including spiritual or transcendental models, psychological models, and physiological models.
These theories seek to provide insight into the subjective nature of NDEs and their potential underlying mechanisms.
Spiritual or Transcendental Models
Many individuals interpret near-death experiences (NDEs) through spiritual or transcendental models, attributing the encounters to connections with divine or metaphysical realms. These models often involve a belief in an afterlife, guiding presence, or encounter with deceased loved ones.
The reported sense of unconditional love and peace during NDEs aligns with many spiritual teachings and reinforces faith-based interpretations. This perception is further amplified by the profound impact NDEs have on individuals’ spirituality, leading to increased altruism and a deeper connection to their inner selves.
Additionally, the cross-cultural aspect of NDE accounts reveals common themes across different religious and spiritual beliefs worldwide. Individuals from diverse backgrounds report similar elements in their near-death experiences, reinforcing the transcendent nature of these occurrences beyond cultural boundaries.
Psychological Models
Psychological models of near-death experiences focus on understanding NDEs through the lens of human psychology and cognitive processes. These models propose that NDEs might be triggered by a combination of psychological factors, such as the brain’s response to extreme stress, altered states of consciousness, or mechanisms related to memory encoding and retrieval.
Research suggests that individuals undergoing NDEs may experience depersonalization, where they feel disconnected from their physical bodies, potentially leading to vivid and emotionally intense experiences that are later recalled with striking clarity.
Moreover, psychological models also explore how cultural conditioning and personal beliefs can shape an individual’s interpretation of the near-death experience. This aspect highlights how subjective perceptions and prior knowledge may influence the content and overall impact of NDEs on an individual’s mental well-being post-experience.
Physiological Models
Physiological models attempt to explain NDEs through brain function and chemistry rather than spiritual or psychological perspectives. These models suggest that NDEs could be a result of anoxia, neurotransmitter release during extreme stress, or disruptions in specific regions of the brain such as the temporal lobes and limbic system.
However, these explanations lack empirical support and have been linked to severe brain injury. The core NDE is believed to be genetically imprinted and triggered by serotonergic mechanisms, challenging current models of the mind while sparking growing interest in exploring the physiological aspects associated with NDEs.
NDE studies seek to understand the physiology behind near-death experiences by examining factors like low oxygen levels in cardiac arrest patients, effects of hallucinogens like psilocybin on conscious experience, and multisensory integration during these events.
The Cross-cultural Aspects of Near Death Experiences
NDEs exhibit commonalities globally, indicating their independence from culture. Studies have revealed cross-cultural and culture-specific features of NDEs. Young children share similar NDE content with adults, underlining the cross-cultural nature of such experiences.
Certain cultures employ drugs in religious practices to induce transcendent feelings akin to NDEs. A study examining eight Kongo near-death experiences from Central Africa supports the existence of universal features within NDEs, reinforcing the notion that cultural boundaries do not confine these phenomena.
Ongoing research delves into the electromagnetic after-effects of NDEs from a cross-cultural perspective, shedding light on how these transcendental encounters transcend societal and geographical divisions.
Historical Reports of Near Death Experiences
Reports of near-death experiences date back to antiquity, with the oldest medical description originating in ancient Greece around 375 BC. These historical accounts illustrate the enduring nature and widespread occurrence of near-death experiences throughout human history.
Additionally, well-known figures such as Carl Jung, Thomas Edison, and Ernest Hemingway have all documented their own personal encounters with near-death experiences. Such historical instances not only provide a glimpse into the longevity of these phenomena but also underscore their impact on individuals across various cultural and temporal contexts.
Historical records offer valuable insight into the prevalence and significance of near-death experiences through centuries past. The documentation of these occurrences by renowned personalities further emphasizes the universal relevance and enduring presence of such profound encounters within human experience.
After-effects of Near Death Experiences
Near Death Experiences (NDEs) leave a lasting impact, with many individuals experiencing depression, strained relationships, and challenges in their professional lives. Post-NDE changes often involve shifts in beliefs and values, leading to decreased fear of death, heightened spiritual connections, and the emergence of psychic abilities or mediumship.
Research indicates that NDE survivors may also encounter blissful emotions and euphoria as residual effects of their near-death encounters.
The aftereffects are not limited to psychological or emotional realms; they can include long-term alterations in an individual’s perception of life, spirituality, and existence itself.
These profound changes offer intriguing insights into human consciousness and the connection between physical experiences and metaphysical phenomena such as NDEs.
Personal Accounts of Near Death Experiences
Personal accounts of near-death experiences offer firsthand insight into the profound and often transformative nature of NDEs. Through narratives such as Anita Moorjani’s and Dr. Eben Alexander’s, readers can gain a deeper understanding of the subjective aspects of these experiences.
Experience: Anita Moorjani
Anita Moorjani had a near-death experience on February 2, 2006 after a four-year battle with cancer. Her profound NDE led to a transformation in her outlook on life and remains an integral part of her public speaking engagements worldwide.
Moorjani’s remarkable story is characterized by an out-of-body encounter and slipping into a coma due to her illness. Her experience, along with those of other near-death survivors such as Dr. Eben Alexander, provides unique insights into this enigmatic phenomenon.
Experience: Dr. Eben Alexander
Dr. Eben Alexander, a neurosurgeon, fell into a deep coma in 2008 due to bacterial meningitis. He documented his profound near-death experience in the book “Proof of Heaven: A Neurosurgeon’s Journey into the Afterlife” (2012).
Dr. Alexander asserts that his encounter with death revealed significant truths about consciousness and the afterlife, claiming that he encountered God during this episode.
He further emphasizes how his near-death experience, while in a coma, has provided insights into the mind-body debate and sparked discussions on the validity of such experiences as proof of an afterlife.
Neuroscience Perspectives on Near-Death Experiences
Neuroscience studies have delved into the brain activity during near-death experiences (NDEs). Research shows that the right temporal-parietal junction, an area of the brain associated with self-awareness and perspective, may play a crucial role in NDEs.
Studies also indicate similarities between NDEs and other altered states of consciousness, such as dreaming or psychedelic experiences. The activation of certain brain regions during these events has prompted scientists to explore how physiological processes could give rise to such profound subjective experiences.
Moreover, investigations into the effects of hypoxia on the brain have provided a potential explanation for some aspects of NDEs. Hypoxic conditions can lead to alterations in cognition and perception, contributing to phenomena akin to NDEs.
Conversely, documentation on patients experiencing vivid memories under surgical anesthesia raises questions about the nature of consciousness and memory formation during periods where traditional neural functions are significantly impaired.
These findings underscore the complex interplay between neuroscience and near-death experiences, offering valuable insights into understanding these enigmatic occurrences.
Conclusion
The near death experiences are reported by individuals who have been comatose or clinically dead but recall vivid and lucid memories. Research into NDEs has provided insights into the functioning of the human brain during critical situations while also acknowledging the personal and cultural influences that shape these profound encounters.